티스토리 뷰
안녕하세요. CloudNet@ K8S Study를 진행하며 해당 내용을 이해하고 공유하기 위해 작성한 글입니다. 해당 내용은 EKS docs와 workshop을 기본으로 정리하였습니다.
실습 환경
# YAML 파일 다운로드
$ curl -O https://s3.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/cloudformation.cloudneta.net/K8S/eks-oneclick4.yaml
# CloudFormation 스택 배포
$ aws cloudformation deploy --template-file eks-oneclick4.yaml --stack-name myeks --parameter-overrides KeyName=kp-hayley3 SgIngressSshCidr=$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip)/32 MyIamUserAccessKeyID=AKIA5... MyIamUserSecretAccessKey='CVNa2...' ClusterBaseName=myeks --region ap-northeast-2
# CloudFormation 스택 배포 완료 후 작업용 EC2 IP 출력
$ aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name myeks --query 'Stacks[*].Outputs[0].OutputValue' --output text
# 작업용 EC2 SSH 접속
$ ssh -i ~/.ssh/kp-hayley3.pem ec2-user@$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name myeks --query 'Stacks[*].Outputs[0].OutputValue' --output text)
기본 설정
# default 네임스페이스 적용
$ kubectl ns default
# (옵션) context 이름 변경
$ NICK=<각자 자신의 닉네임>
$ NICK=hayley
$ kubectl ctx
$ kubectl config rename-context admin@myeks.ap-northeast-2.eksctl.io $NICK@myeks
# ExternalDNS
$ MyDomain=<자신의 도메인>
$ echo "export MyDomain=<자신의 도메인>" >> /etc/profile
$ MyDomain=wellbeconnected.com
$ echo "export MyDomain=wellbeconnected.com" >> /etc/profile
$ MyDnzHostedZoneId=$(aws route53 list-hosted-zones-by-name --dns-name "${MyDomain}." --query "HostedZones[0].Id" --output text)
$ echo $MyDomain, $MyDnzHostedZoneId
$ curl -s -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gasida/PKOS/main/aews/externaldns.yaml
$ MyDomain=$MyDomain MyDnzHostedZoneId=$MyDnzHostedZoneId envsubst < externaldns.yaml | kubectl apply -f -
# kube-ops-view
$ helm repo add geek-cookbook https://geek-cookbook.github.io/charts/
$ helm install kube-ops-view geek-cookbook/kube-ops-view --version 1.2.2 --set env.TZ="Asia/Seoul" --namespace kube-system
$ kubectl patch svc -n kube-system kube-ops-view -p '{"spec":{"type":"LoadBalancer"}}'
$ kubectl annotate service kube-ops-view -n kube-system "external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname=kubeopsview.$MyDomain"
$ echo -e "Kube Ops View URL = http://kubeopsview.$MyDomain:8080/#scale=1.5"
# AWS LB Controller
$ helm repo add eks https://aws.github.io/eks-charts
$ helm repo update
$ helm install aws-load-balancer-controller eks/aws-load-balancer-controller -n kube-system --set clusterName=$CLUSTER_NAME \
--set serviceAccount.create=false --set serviceAccount.name=aws-load-balancer-controller
# 노드 보안그룹 ID 확인
$ NGSGID=$(aws ec2 describe-security-groups --filters Name=group-name,Values='*ng1*' --query "SecurityGroups[*].[GroupId]" --output text)
$ aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress --group-id $NGSGID --protocol '-1' --cidr 192.168.1.100/32프로메테우스 & 그라파나(admin / prom-operator) 설치
# 사용 리전의 인증서 ARN 확인
$ CERT_ARN=`aws acm list-certificates --query 'CertificateSummaryList[].CertificateArn[]' --output text`
$ echo $CERT_ARN
# repo 추가
$ helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
# 파라미터 파일 생성
$ cat <<EOT > monitor-values.yaml
prometheus:
prometheusSpec:
podMonitorSelectorNilUsesHelmValues: false
serviceMonitorSelectorNilUsesHelmValues: false
retention: 5d
retentionSize: "10GiB"
verticalPodAutoscaler:
enabled: true
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: alb
hosts:
- prometheus.$MyDomain
paths:
- /*
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: ip
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTPS":443}, {"HTTP":80}]'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: $CERT_ARN
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/success-codes: 200-399
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-name: myeks-ingress-alb
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/group.name: study
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: '443'
grafana:
defaultDashboardsTimezone: Asia/Seoul
adminPassword: prom-operator
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: alb
hosts:
- grafana.$MyDomain
paths:
- /*
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: ip
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTPS":443}, {"HTTP":80}]'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: $CERT_ARN
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/success-codes: 200-399
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-name: myeks-ingress-alb
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/group.name: study
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: '443'
defaultRules:
create: false
kubeControllerManager:
enabled: false
kubeEtcd:
enabled: false
kubeScheduler:
enabled: false
alertmanager:
enabled: false
EOT
# 배포
$ kubectl create ns monitoring
$ helm install kube-prometheus-stack prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-stack --version 45.27.2 \
--set prometheus.prometheusSpec.scrapeInterval='15s' --set prometheus.prometheusSpec.evaluationInterval='15s' \
-f monitor-values.yaml --namespace monitoring
# Metrics-server 배포
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yamlEKS Node Viewer 설치 : 노드 할당 가능 용량과 요청 request 리소스 표시, 실제 파드 리소스 사용량 X
# go 설치
$ yum install -y go
# EKS Node Viewer 설치 : 현재 ec2 spec에서는 설치에 다소 시간이 소요됨 = 2분 이상
$ go install github.com/awslabs/eks-node-viewer/cmd/eks-node-viewer@latest
# bin 확인 및 사용
$ tree ~/go/bin
$ cd ~/go/bin
$ ./eks-node-viewer
3 nodes (875m/5790m) 15.1% cpu ██████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░ $0.156/h
20 pods (0 pending 20 running 20 bound)
ip-192-168-1-152.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
ip-192-168-3-108.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ████████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
ip-192-168-2-83.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
Press any key to quit
명령 샘플
# Standard usage
$ ./eks-node-viewer
3 nodes (875m/5790m) 15.1% cpu ██████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░ $0.156/h
20 pods (0 pending 20 running 20 bound)
ip-192-168-1-152.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
ip-192-168-3-108.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ████████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
ip-192-168-2-83.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
Press any key to quit
# Display both CPU and Memory Usage
$ ./eks-node-viewer --resources cpu,memory
3 nodes (875m/5790m) 15.1% cpu ██████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░ $
390Mi/10165092Ki 3.9% memory ██░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
20 pods (0 pending 20 running 20 bound)
ip-192-168-1-152.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
memory ██░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
ip-192-168-3-108.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ████████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
memory █░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
ip-192-168-2-83.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
memory █░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
Press any key to quit
# Karenter nodes only
$ ./eks-node-viewer --node-selector "karpenter.sh/provisioner-name"
# Display extra labels, i.e. AZ
$ ./eks-node-viewer --extra-labels topology.kubernetes.io/zone
3 nodes (875m/5790m) 15.1% cpu ██████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░ $0.156/h
20 pods (0 pending 20 running 20 bound)
ip-192-168-1-152.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
ip-192-168-3-108.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ████████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
ip-192-168-2-83.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
Press any key to quit
# Specify a particular AWS profile and region
$ AWS_PROFILE=myprofile AWS_REGION=us-west-2
기본 옵션
# select only Karpenter managed nodes
$ node-selector=karpenter.sh/provisioner-name
# display both CPU and memory
$ resources=cpu,memoryKubernetes autoscaling overview

참고: AWS re:Invent 2022 — Optimizing Amazon EKS for performance and cost on AWS (CON324)
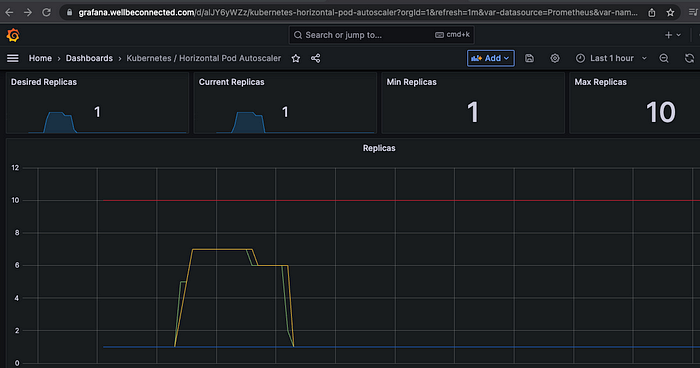
HPA — Horizontal Pod Autoscaler
- kube-ops-view 와 그라파나(17125)에서 모니터링 실습
# Run and expose php-apache server
$ curl -s -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/website/main/content/en/examples/application/php-apache.yaml
$ cat php-apache.yaml | yh
$ kubectl apply -f php-apache.yaml
# 확인
$ kubectl exec -it deploy/php-apache -- cat /var/www/html/index.php
<?php
$x = 0.0001;
for ($i = 0; $i <= 1000000; $i++) {
$x += sqrt($x);
}
echo "OK!";
?>
...
# 모니터링 : 터미널2개 사용
$ watch -d 'kubectl get hpa,pod;echo;kubectl top pod;echo;kubectl top node'
$ kubectl exec -it deploy/php-apache -- top
# 접속
$ PODIP=$(kubectl get pod -l run=php-apache -o jsonpath={.items[0].status.podIP})
$ curl -s $PODIP; echo
OK!HPA 생성 및 부하 발생 후 오토 스케일링 테스트
# Create the HorizontalPodAutoscaler : requests.cpu=200m - 알고리즘
# Since each pod requests 200 milli-cores by kubectl run, this means an average CPU usage of 100 milli-cores.
$ kubectl autoscale deployment php-apache --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
$ kubectl describe hpa
...
Metrics: ( current / target )
resource cpu on pods (as a percentage of request): 0% (1m) / 50%
Min replicas: 1
Max replicas: 10
Deployment pods: 1 current / 1 desired
# HPA 설정 확인
$ kubectl krew install neat
$ kubectl get hpa php-apache -o yaml
$ kubectl get hpa php-apache -o yaml | kubectl neat | yh
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: php-apache
namespace: default
spec:
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- resource:
name: cpu
target:
averageUtilization: 50
type: Utilization
type: Resource
minReplicas: 1
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: php-apache
# 반복 접속 1 (파드1 IP로 접속) >> 증가 확인 후 중지
$ while true;do curl -s $PODIP; sleep 0.5; done
OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!^C
# 반복 접속 2 (서비스명 도메인으로 접속) >> 증가 확인 후 중지 >> 중지 5분 후 파드 갯수 감소 확인
# Run this in a separate terminal
# so that the load generation continues and you can carry on with the rest of the steps
$ kubectl run -i --tty load-generator --rm --image=busybox:1.28 --restart=Never -- /bin/sh -c "while sleep 0.01; do wget -q -O- http://php-apache; done"
OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!OK!O
.....
pod/php-apache-698db99f59-4l6ch 1/1 Running 0 4m9s
pod/php-apache-698db99f59-6rc55 1/1 Running 0 3m24s
pod/php-apache-698db99f59-crnjh 1/1 Running 0 21m
pod/php-apache-698db99f59-h8tss 1/1 Running 0 3m24s
pod/php-apache-698db99f59-m5hzr 1/1 Running 0 4m24s
pod/php-apache-698db99f59-srjr7 1/1 Running 0 4m9s
pod/php-apache-698db99f59-xqv2b 1/1 Running 0 4m24s
...
KEDA — Kubernetes based Event Driven Autoscaler
- 기존의 HPA(Horizontal Pod Autoscaler)는 리소스(CPU, Memory) 메트릭을 기반으로 스케일 여부를 결정하게 됩니다.
- KEDA는 특정 이벤트를 기반으로 스케일 여부를 결정할 수 있습니다.
# KEDA 설치
$ cat <<EOT > keda-values.yaml
metricsServer:
useHostNetwork: true
prometheus:
metricServer:
enabled: true
port: 9022
portName: metrics
path: /metrics
serviceMonitor:
# Enables ServiceMonitor creation for the Prometheus Operator
enabled: true
podMonitor:
# Enables PodMonitor creation for the Prometheus Operator
enabled: true
operator:
enabled: true
port: 8080
serviceMonitor:
# Enables ServiceMonitor creation for the Prometheus Operator
enabled: true
podMonitor:
# Enables PodMonitor creation for the Prometheus Operator
enabled: true
webhooks:
enabled: true
port: 8080
serviceMonitor:
# Enables ServiceMonitor creation for the Prometheus webhooks
enabled: true
EOT
$ kubectl create namespace keda
$ helm repo add kedacore https://kedacore.github.io/charts
$ helm install keda kedacore/keda --version 2.10.2 --namespace keda -f keda-values.yaml
# KEDA 설치 확인
$ kubectl get-all -n keda
$ kubectl get all -n keda
$ kubectl get crd | grep keda
clustertriggerauthentications.keda.sh 2023-05-27T14:42:31Z
scaledjobs.keda.sh 2023-05-27T14:42:31Z
scaledobjects.keda.sh 2023-05-27T14:42:31Z
triggerauthentications.keda.sh 2023-05-27T14:42:31Z
# keda 네임스페이스에 디플로이먼트 생성
$ kubectl apply -f php-apache.yaml -n keda
$ kubectl get pod -n keda
# ScaledObject 정책 생성 : cron
$ cat <<EOT > keda-cron.yaml
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
kind: ScaledObject
metadata:
name: php-apache-cron-scaled
spec:
minReplicaCount: 0
maxReplicaCount: 2
pollingInterval: 30
cooldownPeriod: 300
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: php-apache
triggers:
- type: cron
metadata:
timezone: Asia/Seoul
start: 00,15,30,45 * * * *
end: 05,20,35,50 * * * *
desiredReplicas: "1"
EOT
$ kubectl apply -f keda-cron.yaml -n keda
# 그라파나 대시보드 추가
# 모니터링
$ watch -d 'kubectl get ScaledObject,hpa,pod -n keda'
$ kubectl get ScaledObject -w
# 확인
$ kubectl get ScaledObject,hpa,pod -n keda
NAME SCALETARGETKIND SCALETARGETNAME MIN MAX TRIGGERS AUTHENTICATION READY ACTIVE FALLBACK AGE
scaledobject.keda.sh/php-apache-cron-scaled apps/v1.Deployment php-apache 0 2 cron True True Unknown 77s
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/keda-hpa-php-apache-cron-scaled Deployment/php-apache <unknown>/1 (avg) 1 2 0 77s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/keda-admission-webhooks-68cf687cbf-szj68 1/1 Running 0 3m7s
pod/keda-operator-656478d687-nn4x2 1/1 Running 1 (2m57s ago) 3m7s
pod/keda-operator-metrics-apiserver-7fd585f657-lph24 1/1 Running 0 3m7s
pod/php-apache-698db99f59-4jzgr 1/1 Running 0 16s
$ kubectl get hpa -o jsonpath={.items[0].spec} -n keda | jq
{
"maxReplicas": 2,
"metrics": [
{
"external": {
"metric": {
"name": "s0-cron-Asia-Seoul-00,15,30,45xxxx-05,20,35,50xxxx",
"selector": {
"matchLabels": {
"scaledobject.keda.sh/name": "php-apache-cron-scaled"
}
}
},
"target": {
"averageValue": "1",
"type": "AverageValue"
}
},
"type": "External"
}
],
"minReplicas": 1,
"scaleTargetRef": {
"apiVersion": "apps/v1",
"kind": "Deployment",
"name": "php-apache"
}
}
# KEDA 및 deployment 등 삭제
$ kubectl delete -f keda-cron.yaml -n keda && kubectl delete deploy php-apache -n keda && helm uninstall keda -n keda
$ kubectl delete namespace kedaKEDA 활용 : Karpenter + KEDA로 특정 시간에 AutoScaling
- CA는 ASG 설정을 통해 일정 시간에 노드를 증설하고 감소시킬 수 있으나 Karpenter는 ASG를 사용하지 않기 때문에 불가능하다.
실습 :
- KEDA 사용 (cron을 사용해서 일정 시간에 파드 증가/감소)
- Pod에 affinity.podAntiAffinity 를 사용하고 cpu request 1m으로 설정
- Karpenter가 파드안티어피니티를 확인하고 Pod가 없는 새로운 노드를 증설 → 오버 프로비저닝 Pod의 개수만큼 노드 증설이 보장된다.
# KEDA 설치
$ helm repo add kedacore https://kedacore.github.io/charts
$ helm repo update
$ helm install keda kedacore/keda -n keda --create-namespace
# Karpenter Provisioner
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1alpha5
kind: Provisioner
metadata:
name: karpenter-provisioner
spec:
requirements:
- key: node.kubernetes.io/instance-type
operator: In
values: ["t3.medium", "t3.large", "t3.xlarge"]
- key: "topology.kubernetes.io/zone"
operator: In
values: ["ap-northeast-2a", "ap-northeast-2c"]
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values: ["on-demand"]
limits:
resources:
cpu: "1000"
memory: 1000Gi
ttlSecondsAfterEmpty: 30
labels:
role: ops
provision: karpenter
provider:
securityGroupSelector:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
subnetSelector:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
tags:
Name: karpenter.sh/provisioner-name/karpenter-provisioner
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
# 오버 프로비저닝 Pod
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
replicas: 0
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1m
affinity:
nodeAffinity: # karpenter node 증설을 위한 노드어피니티.
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: provision
operator: In
values:
- karpenter
podAntiAffinity: # 파드 개수만큼 node 증설하기 위한 파드안티어피니티.
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- nginx
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
# KEDA ScaledObject
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
kind: ScaledObject
metadata:
name: keda-over-provioning
spec:
# min / max count
minReplicaCount: 1
maxReplicaCount: 10
# target
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: nginx
triggers:
- type: cron
metadata:
timezone: Asia/Seoul
start: 00 13 * * *
end: 00 21 * * *
desiredReplicas: "5"
# HPA 생성
$ kubectl get hpa
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
keda-hpa-keda-over-provioning Deployment/nginx 1/1 (avg) 1 10 1 17s
# 지정시간이 되면 Karpenter가 Pod, Node 개수 증설함 VPA — Vertical Pod Autoscaler
- pod resources.request을 최대한 최적값으로 수정, HPA와 같이 사용 불가능, 수정 시 파드 재실행
# 코드 다운로드
$ git clone https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler.git
$ cd ~/autoscaler/vertical-pod-autoscaler/
$ tree hack
hack
├── boilerplate.go.txt
├── convert-alpha-objects.sh
├── deploy-for-e2e.sh
├── generate-crd-yaml.sh
├── run-e2e.sh
├── run-e2e-tests.sh
├── update-codegen.sh
├── update-kubernetes-deps-in-e2e.sh
├── update-kubernetes-deps.sh
├── verify-codegen.sh
├── vpa-apply-upgrade.sh
├── vpa-down.sh
├── vpa-process-yaml.sh
├── vpa-process-yamls.sh
├── vpa-up.sh
└── warn-obsolete-vpa-objects.sh
0 directories, 16 files
# openssl 버전 확인
$ openssl version
OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
# openssl 1.1.1 이상 버전 확인
$ yum install openssl11 -y
$ openssl11 version
OpenSSL 1.1.1g FIPS 21 Apr 2020
# 스크립트파일내에 openssl11 수정
$ sed -i 's/openssl/openssl11/g' ~/autoscaler/vertical-pod-autoscaler/pkg/admission-controller/gencerts.sh
# Deploy the Vertical Pod Autoscaler to your cluster with the following command.
$ watch -d kubectl get pod -n kube-system
$ cat hack/vpa-up.sh
#!/bin/bash
# Copyright 2018 The Kubernetes Authors.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
set -o errexit
set -o nounset
set -o pipefail
SCRIPT_ROOT=$(dirname ${BASH_SOURCE})/..
$SCRIPT_ROOT/hack/vpa-process-yamls.sh create
$ ./hack/vpa-up.sh
$ kubectl get crd | grep autoscaling
verticalpodautoscalercheckpoints.autoscaling.k8s.io 2023-05-27T15:17:48Z
verticalpodautoscalers.autoscaling.k8s.io 2023-05-27T15:17:48Z# 모니터링
$ watch -d kubectl top pod
# 공식 예제 배포
$ cd ~/autoscaler/vertical-pod-autoscaler/
$ cat examples/hamster.yaml | yh
---
apiVersion: "autoscaling.k8s.io/v1"
kind: VerticalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: hamster-vpa
spec:
# recommenders
# - name 'alternative'
targetRef:
apiVersion: "apps/v1"
kind: Deployment
name: hamster
resourcePolicy:
containerPolicies:
- containerName: '*'
minAllowed:
cpu: 100m
memory: 50Mi
maxAllowed:
cpu: 1
memory: 500Mi
controlledResources: ["cpu", "memory"]
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hamster
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hamster
replicas: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hamster
spec:
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 65534 # nobody
containers:
- name: hamster
image: registry.k8s.io/ubuntu-slim:0.1
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 50Mi
command: ["/bin/sh"]
args:
- "-c"
- "while true; do timeout 0.5s yes >/dev/null; sleep 0.5s; done"
$ kubectl apply -f examples/hamster.yaml && kubectl get vpa -w
NAME MODE CPU MEM PROVIDED AGE
hamster-vpa 587m 262144k True 2m18s
# 파드 리소스 Requestes 확인
$ kubectl describe pod | grep Requests: -A2
Requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 50Mi
--
Requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 50Mi
--
Requests:
cpu: 1m
Environment: <none>
--
Requests:
cpu: 200m
Environment: <none>
# VPA에 의해 기존 파드 삭제되고 신규 파드가 생성됨
$ kubectl get events --sort-by=".metadata.creationTimestamp" | grep VPA
2m16s Normal EvictedByVPA pod/hamster-5bccbb88c6-s6jkp Pod was evicted by VPA Updater to apply resource recommendation.
76s Normal EvictedByVPA pod/hamster-5bccbb88c6-jc6gq Pod was evicted by VPA Updater to apply resource recommendation.
# 삭제
$ kubectl delete -f examples/hamster.yaml && cd ~/autoscaler/vertical-pod-autoscaler/ && ./hack/vpa-down.sh
CA — Cluster Autoscaler
- Cluster Autoscale 동작을 하기 위한 cluster-autoscaler 파드(디플로이먼트)를 배치합니다.
- Cluster Autoscaler(CA)는 pending 상태인 파드가 존재할 경우, 워커 노드를 스케일 아웃합니다.
- 특정 시간을 간격으로 사용률을 확인하여 스케일 인/아웃을 수행합니다. 그리고 AWS에서는 Auto Scaling Group(ASG)을 사용하여 Cluster Autoscaler를 적용합니다.
Cluster Autoscaler(CA) 설정
# EKS 노드에 이미 아래 tag가 들어가 있음
# k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/enabled : true
# k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/myeks : owned
$ aws ec2 describe-instances --filters Name=tag:Name,Values=$CLUSTER_NAME-ng1-Node --query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].Tags[*]" --output yaml | yh
...
- Key: k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/myeks
Value: owned
- Key: k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/enabled
Value: 'true'
...# 현재 autoscaling(ASG) 정보 확인
# aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='클러스터이름']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" --output table
$ aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups \
--query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" \
--output table
-----------------------------------------------------------------
| DescribeAutoScalingGroups |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
| eks-ng1-d8c42e9a-525d-ab54-5ddf-e8be5d85ff28 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
# MaxSize 6개로 수정
$ export ASG_NAME=$(aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='eks-hayley']].AutoScalingGroupName" --output text)
$ aws autoscaling update-auto-scaling-group --auto-scaling-group-name ${ASG_NAME} --min-size 3 --desired-capacity 3 --max-size 6
# 확인
$ aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='eks-hayley']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" --output table
-----------------------------------------------------------------
| DescribeAutoScalingGroups |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
| eks-ng1-c2c41e26-6213-a429-9a58-02374389d5c3 | 3 | 6 | 3 |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
# 배포 : Deploy the Cluster Autoscaler (CA)
$ curl -s -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/aws/examples/cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yaml
$ sed -i "s/<YOUR CLUSTER NAME>/$CLUSTER_NAME/g" cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yaml
# 확인
$ kubectl get pod -n kube-system | grep cluster-autoscaler
cluster-autoscaler-799b44d94-hv5cz 1/1 Running 0 17s
$ kubectl describe deployments.apps -n kube-system cluster-autoscaler
# (옵션) cluster-autoscaler 파드가 동작하는 워커 노드가 퇴출(evict) 되지 않게 설정
$ kubectl -n kube-system annotate deployment.apps/cluster-autoscaler cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/safe-to-evict="false"
deployment.apps/cluster-autoscaler annotatedSCALE A CLUSTER WITH Cluster Autoscaler(CA)
# 모니터링
$ kubectl get nodes -w
$ while true; do kubectl get node; echo "------------------------------" ; date ; sleep 1; done
$ while true; do aws ec2 describe-instances --query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PrivateIPAdd:PrivateIpAddress,InstanceName:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name}" --filters Name=instance-state-name,Values=running --output text ; echo "------------------------------"; date; sleep 1; done
# Deploy a Sample App
# We will deploy an sample nginx application as a ReplicaSet of 1 Pod
$ cat <<EoF> nginx.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-to-scaleout
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
service: nginx
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx-to-scaleout
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
EoF
$ kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
$ kubectl get deployment/nginx-to-scaleout
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-to-scaleout 1/1 1 1 9s
# Scale our ReplicaSet
# Let’s scale out the replicaset to 15
$ kubectl scale --replicas=15 deployment/nginx-to-scaleout && date
Sun May 28 00:33:16 KST 2023
# 확인
$ kubectl get pods -l app=nginx -o wide --watch
$ kubectl -n kube-system logs -f deployment/cluster-autoscaler
# 노드 자동 증가 확인
$ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-192-168-1-152.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 177m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-2-83.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 177m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-3-108.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 177m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
$ aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups \
--query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" \
--output table
Sun May 28 00:34:23 KST 2023
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-192-168-1-152.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 178m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-1-197.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 14s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-2-174.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 20s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-2-83.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 178m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-3-108.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 178m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-3-210.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 13s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
# 디플로이먼트 삭제
$ kubectl delete -f nginx.yaml && date
# 노드 갯수 축소 : 기본은 10분 후 scale down 됨, 물론 아래 flag 로 시간 수정 가능 >> 그러니 디플로이먼트 삭제 후 10분 기다리고 나서 보자!
# By default, cluster autoscaler will wait 10 minutes between scale down operations,
# you can adjust this using the --scale-down-delay-after-add, --scale-down-delay-after-delete,
# and --scale-down-delay-after-failure flag.
# E.g. --scale-down-delay-after-add=5m to decrease the scale down delay to 5 minutes after a node has been added.
# 터미널1
$ watch -d kubectl get node- CA 문제점 : 하나의 자원에 대해 두군데 (AWS ASG vs AWS EKS)에서 각자의 방식으로 관리해서 관리 정보가 서로 동기화되지 않아 다양한 문제 발생
CPA — Cluster Proportional Autoscaler
$ helm repo add cluster-proportional-autoscaler https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/cluster-proportional-autoscaler
# CPA규칙을 설정하고 helm차트를 릴리즈 필요
$ helm upgrade --install cluster-proportional-autoscaler cluster-proportional-autoscaler/cluster-proportional-autoscaler
# nginx 디플로이먼트 배포
$ cat <<EOT > cpa-nginx.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
resources:
limits:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "64Mi"
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "64Mi"
ports:
- containerPort: 80
EOT
$ kubectl apply -f cpa-nginx.yaml
# CPA 규칙 설정
$ cat <<EOF > cpa-values.yaml
config:
ladder:
nodesToReplicas:
- [1, 1]
- [2, 2]
- [3, 3]
- [4, 3]
- [5, 5]
options:
namespace: default
target: "deployment/nginx-deployment"
EOF
# 모니터링
$ watch -d kubectl get pod
# helm 업그레이드
$ helm upgrade --install cluster-proportional-autoscaler -f cpa-values.yaml cluster-proportional-autoscaler/cluster-proportional-autoscaler
# 노드 5개로 증가
# export ASG_NAME=$(aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='eks-hayley']].AutoScalingGroupName" --output text)
# aws autoscaling update-auto-scaling-group --auto-scaling-group-name ${ASG_NAME} --min-size 5 --desired-capacity 5 --max-size 5
$ aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='eks-hayley']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" --output table
-----------------------------------------------------------------
| DescribeAutoScalingGroups |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
| eks-ng1-d8c42e9a-525d-ab54-5ddf-e8be5d85ff28 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
# 노드 4개로 축소
$ aws autoscaling update-auto-scaling-group --auto-scaling-group-name ${ASG_NAME} --min-size 4 --desired-capacity 4 --max-size 4
$ aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='eks-hayley']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" --output table
-----------------------------------------------------------------
| DescribeAutoScalingGroups |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
| eks-ng1-d8c42e9a-525d-ab54-5ddf-e8be5d85ff28 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
# 삭제
$ helm uninstall cluster-proportional-autoscaler && kubectl delete -f cpa-nginx.yamlKarpenter : K8S Native AutoScaler & Fargate
- Karpenter 실습 환경 준비를 위해서 현재 EKS 실습 환경 전부 삭제 후 신규 배포합니다.
- 참고 영상 : 오픈 소스 Karpenter를 활용한 Amazon EKS 확장 운영 전략 | 신재현, 무신사
- 작동 방식
— 모니터링 → (스케줄링 안된 Pod 발견) → 스펙 평가 → 생성 ⇒ Provisioning
— 모니터링 → (비어있는 노드 발견) → 제거 ⇒ Deprovisioning
$ helm uninstall -n kube-system kube-ops-view
$ helm uninstall -n monitoring kube-prometheus-stack$ eksctl delete cluster --name $CLUSTER_NAME && aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name $CLUSTER_NAME
# YAML 파일 다운로드
$ curl -O https://s3.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/cloudformation.cloudneta.net/K8S/karpenter-preconfig.yaml
# CloudFormation 스택 배포
예시) aws cloudformation deploy --template-file karpenter-preconfig.yaml --stack-name myeks2 --parameter-overrides KeyName=kp-hayley3 SgIngressSshCidr=$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip)/32 MyIamUserAccessKeyID=**AKIA5...** MyIamUserSecretAccessKey=**'CVNa2...'ClusterBaseName=**myeks2 --region ap-northeast-2
# CloudFormation 스택 배포 완료 후 작업용 EC2 IP 출력
$ aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name myeks2 --query 'Stacks[*].Outputs[0].OutputValue' --output text
# 작업용 EC2 SSH 접속
$ ssh -i ~/.ssh/kp-hayley3 ec2-user@$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name myeks2 --query 'Stacks[*].Outputs[0].OutputValue' --output text)
- 배포 전 사전 확인 & eks-node-viewer 설치
# IP 주소 확인 : 172.30.0.0/16 VPC 대역에서 172.30.1.0/24 대역을 사용 중
$ ip -br -c addr
lo UNKNOWN 127.0.0.1/8 ::1/128
eth0 UP 172.30.1.100/24 fe80::c8:f8ff:fe68:9368/64
docker0 DOWN 172.17.0.1/16
# EKS Node Viewer 설치 : 현재 ec2 spec에서는 설치에 다소 시간이 소요됨 = 2분 이상
$ go install github.com/awslabs/eks-node-viewer/cmd/eks-node-viewer@latest
# [터미널1] bin 확인 및 사용
$ tree ~/go/bin
/root/go/bin
└── eks-node-viewer
0 directories, 1 file
$ cd ~/go/bin
$ ./eks-node-viewer -h
$ ./eks-node-viewer # EKS 배포 완료 후 실행# 환경변수 정보 확인
$ export | egrep 'ACCOUNT|AWS_|CLUSTER' | egrep -v 'SECRET|KEY'
# 환경변수 설정
$ export KARPENTER_VERSION=v0.27.5
$ export TEMPOUT=$(mktemp)
$ echo $KARPENTER_VERSION $CLUSTER_NAME $AWS_DEFAULT_REGION $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID $TEMPOUT
_REGION $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID
eks-hayley ap-northeast-2 90XXXXXXXXXX
# CloudFormation 스택으로 IAM Policy, Role, EC2 Instance Profile 생성 : 3분 정도 소요
$ curl -fsSL https://karpenter.sh/"${KARPENTER_VERSION}"/getting-started/getting-started-with-karpenter/cloudformation.yaml > $TEMPOUT \
&& aws cloudformation deploy \
--stack-name "Karpenter-${CLUSTER_NAME}" \
--template-file "${TEMPOUT}" \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--parameter-overrides "ClusterName=${CLUSTER_NAME}"
# 클러스터 생성 : myeks2 EKS 클러스터 생성 19분 정도 소요
$ eksctl create cluster -f - <<EOF
---
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
metadata:
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
region: ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}
version: "1.24"
tags:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
iam:
withOIDC: true
serviceAccounts:
- metadata:
name: karpenter
namespace: karpenter
roleName: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-karpenter
attachPolicyARNs:
- arn:aws:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:policy/KarpenterControllerPolicy-${CLUSTER_NAME}
roleOnly: true
iamIdentityMappings:
- arn: "arn:aws:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:role/KarpenterNodeRole-${CLUSTER_NAME}"
username: system:node:{{EC2PrivateDNSName}}
groups:
- system:bootstrappers
- system:nodes
managedNodeGroups:
- instanceType: m5.large
amiFamily: AmazonLinux2
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-ng
desiredCapacity: 2
minSize: 1
maxSize: 10
iam:
withAddonPolicies:
externalDNS: true
## Optionally run on fargate
# fargateProfiles:
# - name: karpenter
# selectors:
# - namespace: karpenter
EOF
# eks 배포 확인
$ eksctl get cluster
NAME REGION EKSCTL CREATED
eks-hayley ap-northeast-2 True
$ eksctl get nodegroup --cluster $CLUSTER_NAME
CLUSTER NODEGROUP STATUS CREATED MIN SIZE MAX SIZE DESIRED CAPACITY INSTANCE TYPE IMAGE ID ASG NAME TYPE
eks-hayley eks-hayley-ng ACTIVE 2023-05-27T21:49:56Z 1 10 m5.large AL2_x86_64 eks-eks-hayley-ng-5cc42f98-3e9c-2cd6-d4f7-23dc5dbacdb7 managed
$ eksctl get iamidentitymapping --cluster $CLUSTER_NAME
ARN USERNAME GROUPS ACCOUNT
arn:aws:iam::90XXXXXXXXXX:role/KarpenterNodeRole-eks-hayley system:node:{{EC2PrivateDNSName}} system:bootstrappers,system:nodes
arn:aws:iam::90XXXXXXXXXX:role/eksctl-eks-hayley-nodegroup-eks-h-NodeInstanceRole-109ZD28N1RH67 system:node:{{EC2PrivateDNSName}} system:bootstrappers,system:nodes
$ eksctl get iamserviceaccount --cluster $CLUSTER_NAME
NAMESPACE NAME ROLE ARN
karpenter karpenter arn:aws:iam::90XXXXXXXXXX:role/eks-hayley-karpenter
kube-system aws-node arn:aws:iam::90XXXXXXXXXX:role/eksctl-eks-hayley-addon-iamserviceaccount-ku-Role1-GNQNXWPQMSA
$ eksctl get addon --cluster $CLUSTER_NAME
--cluster $CLUSTER_NAME
2023-05-28 07:02:38 [ℹ] Kubernetes version "1.24" in use by cluster "eks-hayley"
2023-05-28 07:02:38 [ℹ] getting all addons
No addons found
# [터미널1] eks-node-viewer
cd ~/go/bin && ./eks-node-viewer
2 nodes (450m/3860m) 11.7% cpu █████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░ $0.236/hour |
6 pods (0 pending 6 running 6 bound)
ip-192-168-33-157.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ██████░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
ip-192-168-7-78.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ██░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░░
# k8s 확인
$ kubectl cluster-info
Kubernetes control plane is running at https://6B9D9062923DC8BB07F647ED98341FED.yl4.ap-northeast-2.eks.amazonaws.com
CoreDNS is running at https://6B9D9062923DC8BB07F647ED98341FED.yl4.ap-northeast-2.eks.amazonaws.com/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
$ kubectl get node --label-columns=node.kubernetes.io/instance-type,eks.amazonaws.com/capacityType,topology.kubernetes.io/zone
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INSTANCE-TYPE CAPACITYTYPE ZONE
ip-192-168-33-157.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 11m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 m5.large ON_DEMAND ap-northeast-2c
ip-192-168-7-78.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 11m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 m5.large ON_DEMAND ap-northeast-2a
$ kubectl get pod -n kube-system -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
aws-node-nmfgg 1/1 Running 0 11m 192.168.7.78 ip-192-168-7-78.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
aws-node-rhng5 1/1 Running 0 11m 192.168.33.157 ip-192-168-33-157.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
coredns-dc4979556-nnpc4 1/1 Running 0 19m 192.168.51.77 ip-192-168-33-157.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
coredns-dc4979556-vfqv4 1/1 Running 0 19m 192.168.46.95 ip-192-168-33-157.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
kube-proxy-s47jn 1/1 Running 0 11m 192.168.33.157 ip-192-168-33-157.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
kube-proxy-t5kzr 1/1 Running 0 11m 192.168.7.78 ip-192-168-7-78.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
$ kubectl describe cm -n kube-system aws-auth
...
mapRoles:
----
- groups:
- system:bootstrappers
- system:nodes
rolearn: arn:aws:iam::90XXXXXXXXXX:role/KarpenterNodeRole-eks-hayley
username: system:node:{{EC2PrivateDNSName}}
- groups:
- system:bootstrappers
- system:nodes
rolearn: arn:aws:iam::90XXXXXXXXXX:role/eksctl-eks-hayley-nodegroup-eks-h-NodeInstanceRole-109ZD28N1RH67
username: system:node:{{EC2PrivateDNSName}}
...
# 카펜터 설치를 위한 환경 변수 설정 및 확인
$ export CLUSTER_ENDPOINT="$(aws eks describe-cluster --name ${CLUSTER_NAME} --query "cluster.endpoint" --output text)"
$ export KARPENTER_IAM_ROLE_ARN="arn:aws:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:role/${CLUSTER_NAME}-karpenter"
$ echo $CLUSTER_ENDPOINT $KARPENTER_IAM_ROLE_ARN
# service-linked-role 생성 확인 : 만들어있는것을 확인하는 거라 아래 에러 출력이 정상!
# If the role has already been successfully created, you will see:
# An error occurred (InvalidInput) when calling the CreateServiceLinkedRole operation: Service role name AWSServiceRoleForEC2Spot has been taken in this account, please try a different suffix.
$ aws iam create-service-linked-role --aws-service-name spot.amazonaws.com || true
An error occurred (InvalidInput) when calling the CreateServiceLinkedRole operation: Service role name AWSServiceRoleForEC2Spot has been taken in this account, please try a different suffix.
# docker logout : Logout of docker to perform an unauthenticated pull against the public ECR
$ docker logout public.ecr.aws
Removing login credentials for public.ecr.aws
# karpenter 설치
$ helm upgrade --install karpenter oci://public.ecr.aws/karpenter/karpenter --version ${KARPENTER_VERSION} --namespace karpenter --create-namespace \
--set serviceAccount.annotations."eks\.amazonaws\.com/role-arn"=${KARPENTER_IAM_ROLE_ARN} \
--set settings.aws.clusterName=${CLUSTER_NAME} \
--set settings.aws.defaultInstanceProfile=KarpenterNodeInstanceProfile-${CLUSTER_NAME} \
--set settings.aws.interruptionQueueName=${CLUSTER_NAME} \
--set controller.resources.requests.cpu=1 \
--set controller.resources.requests.memory=1Gi \
--set controller.resources.limits.cpu=1 \
--set controller.resources.limits.memory=1Gi \
--wait
# 확인
$ kubectl get-all -n karpenter
$ kubectl get all -n karpenter
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/karpenter-6548d6ccd4-h7ds7 1/1 Running 0 24s
pod/karpenter-6548d6ccd4-l9m58 1/1 Running 0 24s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/karpenter ClusterIP 10.100.75.216 <none> 8080/TCP,443/TCP 24s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/karpenter 2/2 2 2 24s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/karpenter-6548d6ccd4 2 2 2 24s
$ kubectl get cm -n karpenter karpenter-global-settings -o jsonpath={.data} | jq
{
"aws.clusterEndpoint": "",
"aws.clusterName": "eks-hayley",
"aws.defaultInstanceProfile": "KarpenterNodeInstanceProfile-eks-hayley",
"aws.enableENILimitedPodDensity": "true",
"aws.enablePodENI": "false",
"aws.interruptionQueueName": "eks-hayley",
"aws.isolatedVPC": "false",
"aws.nodeNameConvention": "ip-name",
"aws.vmMemoryOverheadPercent": "0.075",
"batchIdleDuration": "1s",
"batchMaxDuration": "10s",
"featureGates.driftEnabled": "false"
}
$ kubectl get crd | grep karpenter
awsnodetemplates.karpenter.k8s.aws 2023-05-27T22:06:07Z
provisioners.karpenter.sh 2023-05-27T22:06:07Z- Create Provisioner : 관리 리소스는 securityGroupSelector와 subnetSelector로 찾음, ttlSecondsAfterEmpty(미사용 노드 정리, 데몬셋 제외)
$ cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1alpha5
kind: Provisioner
metadata:
name: default
spec:
requirements:
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values: ["spot"]
limits:
resources:
cpu: 1000
providerRef:
name: default
ttlSecondsAfterEmpty: 30
---
apiVersion: karpenter.k8s.aws/v1alpha1
kind: AWSNodeTemplate
metadata:
name: default
spec:
subnetSelector:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
securityGroupSelector:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
EOF
# 확인
$ kubectl get awsnodetemplates,provisioners
NAME AGE
awsnodetemplate.karpenter.k8s.aws/default 4s
NAME AGE
provisioner.karpenter.sh/default 4s- Add optional monitoring with Grafana
#
$ helm repo add grafana-charts https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts
$ helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
$ helm repo update
$ kubectl create namespace monitoring
# 프로메테우스 설치
$ curl -fsSL https://karpenter.sh/"${KARPENTER_VERSION}"/getting-started/getting-started-with-karpenter/prometheus-values.yaml | tee prometheus-values.yaml
$ helm install --namespace monitoring prometheus prometheus-community/prometheus --values prometheus-values.yaml --set alertmanager.enabled=false
# 그라파나 설치
$ curl -fsSL https://karpenter.sh/"${KARPENTER_VERSION}"/getting-started/getting-started-with-karpenter/grafana-values.yaml | tee grafana-values.yaml
$ helm install --namespace monitoring grafana grafana-charts/grafana --values grafana-values.yaml --set service.type=LoadBalancer
# admin 암호
$ kubectl get secret --namespace monitoring grafana -o jsonpath="{.data.admin-password}" | base64 --decode ; echo
# 그라파나 접속
$ kubectl annotate service grafana -n monitoring "external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname=grafana.$MyDomain"
$ echo -e "grafana URL = http://grafana.$MyDomain"- First Use
# pause 파드 1개에 CPU 1개 최소 보장 할당
$ cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: inflate
spec:
replicas: 0
selector:
matchLabels:
app: inflate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: inflate
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
containers:
- name: inflate
image: public.ecr.aws/eks-distro/kubernetes/pause:3.7
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
EOF
$ kubectl scale deployment inflate --replicas 5
$ kubectl logs -f -n karpenter -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter -c controller
2023-05-27T22:12:26.323Z DEBUG controller.provisioner.cloudprovider discovered ami {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "ami": "ami-0a31a3ce85ee4a8e6", "query": "/aws/service/eks/optimized-ami/1.24/amazon-linux-2-arm64/recommended/image_id"}
2023-05-27T22:12:26.464Z DEBUG controller.provisioner.cloudprovider created launch template {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "launch-template-name": "karpenter.k8s.aws/17591139823422091228", "launch-template-id": "lt-0c771f82c7a6d4f2f"}
2023-05-27T22:12:29.053Z INFO controller.provisioner.cloudprovider launched instance {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "id": "i-0ae3d1e7783413a89", "hostname": "ip-192-168-115-185.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal", "instance-type": "c4.2xlarge", "zone": "ap-northeast-2a", "capacity-type": "spot", "capacity": {"cpu":"8","ephemeral-storage":"20Gi","memory":"14208Mi","pods":"58"}}
...
# 스팟 인스턴스 확인!
$ aws ec2 describe-spot-instance-requests --filters "Name=state,Values=active" --output table
$ kubectl get node -l karpenter.sh/capacity-type=spot -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.labels}' | jq
$ kubectl get node --label-columns=eks.amazonaws.com/capacityType,karpenter.sh/capacity-type,node.kubernetes.io/instance-type
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION CAPACITYTYPE CAPACITY-TYPE INSTANCE-TYPE
ip-192-168-115-185.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal NotReady <none> 33s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 spot c4.2xlarge
ip-192-168-33-157.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 21m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 ON_DEMAND m5.large
ip-192-168-7-78.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 21m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 ON_DEMAND m5.large m5.large- Scale down deployment : 30초 후(ttlSecondsAfterEmpty) Karpenter는 현재 비어 있는 노드를 종료함
# Now, delete the deployment. After 30 seconds (ttlSecondsAfterEmpty), Karpenter should terminate the now empty nodes.
$ kubectl delete deployment inflate
$ kubectl logs -f -n karpenter -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter -c controller
2023-05-27T22:12:26.296Z DEBUG controller.provisioner.cloudprovider discovered ami {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "ami": "ami-021b63322f1c5fc23", "query": "/aws/service/eks/optimized-ami/1.24/amazon-linux-2-gpu/recommended/image_id"}
2023-05-27T22:12:26.323Z DEBUG controller.provisioner.cloudprovider discovered ami {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "ami": "ami-0a31a3ce85ee4a8e6", "query": "/aws/service/eks/optimized-ami/1.24/amazon-linux-2-arm64/recommended/image_id"}
2023-05-27T22:12:26.464Z DEBUG controller.provisioner.cloudprovider created launch template {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "launch-template-name": "karpenter.k8s.aws/17591139823422091228", "launch-template-id": "lt-0c771f82c7a6d4f2f"}
2023-05-27T22:12:29.053Z INFO controller.provisioner.cloudprovider launched instance {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "id": "i-0ae3d1e7783413a89", "hostname": "ip-192-168-115-185.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal", "instance-type": "c4.2xlarge", "zone": "ap-northeast-2a", "capacity-type": "spot", "capacity": {"cpu":"8","ephemeral-storage":"20Gi","memory":"14208Mi","pods":"58"}}
2023-05-27T22:14:08.853Z DEBUG controller.node added TTL to empty node {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "node": "ip-192-168-115-185.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal"}
- Consolidation : 활용도가 낮은 컴퓨팅 인스턴스에서 실행되는 워크로드가 더 적은 수의 인스턴스로 압축되도록 지속적으로 최적화 함
#
$ kubectl delete provisioners default
$ cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1alpha5
kind: Provisioner
metadata:
name: default
spec:
consolidation:
enabled: true
labels:
type: karpenter
limits:
resources:
cpu: 1000
memory: 1000Gi
providerRef:
name: default
requirements:
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values:
- on-demand
- key: node.kubernetes.io/instance-type
operator: In
values:
- c5.large
- m5.large
- m5.xlarge
EOF
#
$ cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: inflate
spec:
replicas: 0
selector:
matchLabels:
app: inflate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: inflate
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
containers:
- name: inflate
image: public.ecr.aws/eks-distro/kubernetes/pause:3.7
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
EOF
$ kubectl scale deployment inflate --replicas 12
$ kubectl logs -f -n karpenter -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter -c controller
2023-05-27T22:14:53.614Z INFO controller.provisioner.cloudprovider launched instance {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "id": "i-0589886c222795746", "hostname": "ip-192-168-9-235.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal", "instance-type": "m5.xlarge", "zone": "ap-northeast-2a", "capacity-type": "on-demand", "capacity": {"cpu":"4","ephemeral-storage":"20Gi","memory":"15155Mi","pods":"58"}}
2023-05-27T22:14:53.615Z INFO controller.provisioner.cloudprovider launched instance {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "id": "i-048beb4bae026be21", "hostname": "ip-192-168-160-30.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal", "instance-type": "m5.xlarge", "zone": "ap-northeast-2d", "capacity-type": "on-demand", "capacity": {"cpu":"4","ephemeral-storage":"20Gi","memory":"15155Mi","pods":"58"}}
2023-05-27T22:14:53.615Z INFO controller.provisioner.cloudprovider launched instance {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "id": "i-091ef7a24a6e53c10", "hostname": "ip-192-168-164-160.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal", "instance-type": "m5.xlarge", "zone": "ap-northeast-2d", "capacity-type": "on-demand", "capacity": {"cpu":"4","ephemeral-storage":"20Gi","memory":"15155Mi","pods":"58"}}
2023-05-27T22:14:53.615Z INFO controller.provisioner.cloudprovider launched instance {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "id": "i-0ae94c1b6dc6bac64", "hostname": "ip-192-168-13-243.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal", "instance-type": "m5.xlarge", "zone": "ap-northeast-2a", "capacity-type": "on-demand", "capacity": {"cpu":"4","ephemeral-storage":"20Gi","memory":"15155Mi","pods":"58"}}
# 인스턴스 확인
# This changes the total memory request for this deployment to around 12Gi,
# which when adjusted to account for the roughly 600Mi reserved for the kubelet on each node means that this will fit on 2 instances of type m5.large:
$ kubectl get node -l type=karpenter
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-192-168-13-243.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal NotReady <none> 28s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-160-30.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal NotReady <none> 28s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-164-160.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal NotReady <none> 28s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-9-235.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal NotReady <none> 28s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
$ kubectl get node --label-columns=eks.amazonaws.com/capacityType,karpenter.sh/capacity-type
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION CAPACITYTYPE CAPACITY-TYPE
ip-192-168-13-243.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 64s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 on-demand
ip-192-168-160-30.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 64s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 on-demand
ip-192-168-164-160.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 64s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 on-demand
ip-192-168-33-157.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 24m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 ON_DEMAND
ip-192-168-7-78.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 24m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 ON_DEMAND
ip-192-168-9-235.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 64s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 on-demand
$ kubectl get node --label-columns=node.kubernetes.io/instance-type,topology.kubernetes.io/zone
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INSTANCE-TYPE ZONE
ip-192-168-13-243.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 44s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 m5.xlarge ap-northeast-2a
ip-192-168-160-30.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 44s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 m5.xlarge ap-northeast-2d
ip-192-168-164-160.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 44s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 m5.xlarge ap-northeast-2d
ip-192-168-33-157.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 24m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 m5.large ap-northeast-2c
ip-192-168-7-78.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 24m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 m5.large ap-northeast-2a
ip-192-168-9-235.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 44s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 m5.xlarge ap-northeast-2a
# Next, scale the number of replicas back down to 5:
$ kubectl scale deployment inflate --replicas 5
deployment.apps/inflate scaled
# The output will show Karpenter identifying specific nodes to cordon, drain and then terminate:
$ kubectl logs -f -n karpenter -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter -c controller
2023-05-27T22:14:53.615Z INFO controller.provisioner.cloudprovider launched instance {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "id": "i-091ef7a24a6e53c10", "hostname": "ip-192-168-164-160.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal", "instance-type": "m5.xlarge", "zone": "ap-northeast-2d", "capacity-type": "on-demand", "capacity": {"cpu":"4","ephemeral-storage":"20Gi","memory":"15155Mi","pods":"58"}}
2023-05-27T22:14:53.615Z INFO controller.provisioner.cloudprovider launched instance {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "id": "i-0ae94c1b6dc6bac64", "hostname": "ip-192-168-13-243.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal", "instance-type": "m5.xlarge", "zone": "ap-northeast-2a", "capacity-type": "on-demand", "capacity": {"cpu":"4","ephemeral-storage":"20Gi","memory":"15155Mi","pods":"58"}}
2023-05-27T22:16:17.418Z DEBUG controller deleted launch template {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "launch-template": "karpenter.k8s.aws/17591139823422091228"}
2023-05-27T22:16:17.515Z DEBUG controller deleted launch template {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "launch-template": "karpenter.k8s.aws/12282441933135587723"}
2023-05-27T22:16:36.620Z INFO controller.deprovisioning deprovisioning via consolidation delete, terminating 2 machines ip-192-168-9-235.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal/m5.xlarge/on-demand, ip-192-168-160-30.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal/m5.xlarge/on-demand {"commit": "698f22f-dirty"}
2023-05-27T22:16:36.664Z INFO controller.termination cordoned node {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "node": "ip-192-168-9-235.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal"}
2023-05-27T22:16:36.676Z INFO controller.termination cordoned node {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "node": "ip-192-168-160-30.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal"}
2023-05-27T22:16:37.032Z INFO controller.termination deleted node {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "node": "ip-192-168-9-235.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal"}
2023-05-27T22:16:37.033Z INFO controller.termination deleted node {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "node": "ip-192-168-160-30.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal"}
# Next, scale the number of replicas back down to 1
$ kubectl scale deployment inflate --replicas 1
$ kubectl logs -f -n karpenter -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter -c controller
2023-05-27T22:06:17.335Z INFO controller Starting server {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "path": "/metrics", "kind": "metrics", "addr": "[::]:8080"}
2023-05-27T22:06:17.335Z INFO controller Starting server {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "kind": "health probe", "addr": "[::]:8081"}
I0527 22:06:17.437038 1 leaderelection.go:248] attempting to acquire leader lease karpenter/karpenter-leader-election...
2023-05-27T22:06:17.487Z INFO controller Starting informers... {"commit": "698f22f-dirty"}
2023-05-27T22:17:13.770Z INFO controller.deprovisioning deprovisioning via consolidation delete, terminating 1 machines ip-192-168-164-160.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal/m5.xlarge/on-demand {"commit": "698f22f-dirty"}
2023-05-27T22:17:13.804Z INFO controller.termination cordoned node {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "node": "ip-192-168-164-160.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal"}
2023-05-27T22:17:14.101Z INFO controller.termination deleted node {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "node": "ip-192-168-164-160.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal"}
2023-05-27T22:17:30.900Z INFO controller.deprovisioning deprovisioning via consolidation replace, terminating 1 machines ip-192-168-13-243.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal/m5.xlarge/on-demand and replacing with on-demand machine from types c5.large, m5.large {"commit": "698f22f-dirty"}
2023-05-27T22:17:30.924Z INFO controller.deprovisioning launching machine with 1 pods requesting {"cpu":"1125m","pods":"4"} from types c5.large, m5.large{"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default"}
2023-05-27T22:17:31.248Z DEBUG controller.deprovisioning.cloudprovider created launch template {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "launch-template-name": "karpenter.k8s.aws/12282441933135587723", "launch-template-id": "lt-0c841aec3221d8248"}
2023-05-27T22:17:33.253Z INFO controller.deprovisioning.cloudprovider launched instance {"commit": "698f22f-dirty", "provisioner": "default", "id": "i-03ecffed729ed1b03", "hostname": "ip-192-168-113-217.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal", "instance-type": "c5.large", "zone": "ap-northeast-2a", "capacity-type": "on-demand", "capacity": {"cpu":"2","ephemeral-storage":"20Gi","memory":"3788Mi","pods":"29"}}
# 인스턴스 확인
$ kubectl get node -l type=karpenter
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-192-168-113-217.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal NotReady <none> 27s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-13-243.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready,SchedulingDisabled <none> 3m7s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
$ kubectl get node --label-columns=eks.amazonaws.com/capacityType,karpenter.sh/capacity-type
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION CAPACITYTYPE CAPACITY-TYPE
ip-192-168-113-217.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 46s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 on-demand
ip-192-168-33-157.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 27m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 ON_DEMAND
ip-192-168-7-78.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 27m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 ON_DEMAND
$ kubectl get node --label-columns=node.kubernetes.io/instance-type,topology.kubernetes.io/zone
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INSTANCE-TYPE ZONE
ip-192-168-113-217.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 58s v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 c5.large ap-northeast-2a
ip-192-168-33-157.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 27m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 m5.large ap-northeast-2c
ip-192-168-7-78.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 27m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954 m5.large ap-northeast-2a
# 삭제
$ kubectl delete deployment inflate- 삭제
#
$ kubectl delete svc -n monitoring grafana
$ helm uninstall -n kube-system kube-ops-view
$ helm uninstall karpenter --namespace karpenter
# 위 삭제 완료 후 아래 삭제
$ aws ec2 describe-launch-templates --filters Name=tag:eks:cluster-name,Values=${CLUSTER_NAME} |
jq -r ".LaunchTemplates[].LaunchTemplateName" |
xargs -I{} aws ec2 delete-launch-template --launch-template-name {}
# 클러스터 삭제
$ eksctl delete cluster --name "${CLUSTER_NAME}"
#
$ aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name "Karpenter-${CLUSTER_NAME}"
# 위 삭제 완료 후 아래 삭제
$ aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name ${CLUSTER_NAME}
blog migration project
written in 2023.5.28
https://medium.com/techblog-hayleyshim/aws-eks-autoscaling-92c429f16e6f
'IT > Infra&Cloud' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [aws] EKS Automation (0) | 2023.10.30 |
|---|---|
| [aws] EKS Security (0) | 2023.10.30 |
| [aws] EKS Observability (0) | 2023.10.29 |
| [aws] EKS Storage & Node (0) | 2023.10.29 |
| [aws] EKS Networking (0) | 2023.10.29 |
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
TAG
- S3
- 혼공파
- GCP
- AI Engineering
- autoscaling
- PYTHON
- terraform
- k8s calico
- 파이썬
- 혼공챌린지
- cni
- EKS
- k8s cni
- IaC
- SDWAN
- NFT
- ai 엔지니어링
- 혼공단
- cloud
- k8s
- operator
- GKE
- handson
- CICD
- 도서
- AWS
- AI
- VPN
- security
- NW
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
글 보관함
