티스토리 뷰
안녕하세요, k8s istio를 학습한 내용을 공유합니다.
[개념](feat.Gemini)
🏗️ Istio의 역할: 도시 교통 통제 시스템
Istio는 컨테이너화된 마이크로서비스 (도시의 건물이나 서비스)들이 서로 통신할 때 발생하는 모든 복잡한 문제를 해결해 줍니다.
| Istio 개념 | 교통 통제 시스템 비유 | 하는 일 (쉽게) |
| 트래픽 관리 | 신호등, 교차로 규칙 | 요청을 원하는 서비스로 정확히 보내고, 속도나 비중을 조절합니다. |
| 보안 | 경찰 검문소, 보안 게이트 | 서비스 간 통신을 안전하게 암호화하고, 통과할 자격이 있는지 확인합니다. |
| 정책 관리 | 통행료, 진입 제한 구역 | 특정 조건(예: 사용자 유형)에 따라 접근을 허용하거나 거부하는 규칙을 적용합니다. |
| 모니터링 & 로깅 | CCTV, 교통량 센서 | 통신이 잘 되는지 실시간으로 관찰하고, 문제가 생기면 기록합니다. |
| 장애 복구 & 회복력 | 우회로, 긴급 복구팀 | 서비스가 다운되거나 응답이 느릴 때, 자동으로 재시도하거나 다른 경로로 돌려줍니다. |
🛣️ Data Plane (데이터 영역): 도로 위 차량과 통제 요원
Data Plane은 실제 서비스 요청(트래픽)이 오가는 영역입니다.
- 역할: 워크로드(서비스) 간의 모든 통신을 처리하고 중재합니다.
- 비유: 서비스를 요청하는 모든 차량(트래픽)과 그 차량을 통제하는 도로 위의 통제 요원들입니다.
Data Plane - Proxy (Envoy): 각 서비스에 붙은 개인 비서/통제 요원
- Envoy는 고성능의 작은 프록시입니다.
- 사이드카 패턴은 마치 각 서비스(건물) 옆에 개인 비서처럼 딱 붙어 있는 형태를 말합니다.
- 하는 일: 서비스에 들어오고 나가는 모든 트래픽을 가로채서(Intercept) Control Plane에서 받은 규칙대로 처리합니다. (예: "이 요청은 저기로 보내", "이 요청은 보안 검사해", "응답이 느리면 3번 더 시도해")
🚦 Control Plane (제어 영역): 교통 관제 센터 (istiod)
Control Plane은 Data Plane이 잘 작동하도록 규칙을 만들고 지시를 내리는 중앙 통제실입니다.
- 핵심 컴포넌트: 과거 여러 개의 컴포넌트(Pilot, Citadel, Gallery)가 istiod라는 하나의 관제 센터로 통합되었습니다.
1. Pilot: 교통 계획 및 길 안내
- 역할: Data Plane의 Envoy 프록시들에게 어떻게 트래픽을 라우팅(길 안내)할지 규칙을 전달합니다.
- 예시: "새로운 버전의 서비스로 트래픽의 10만 보내라", "미국발 요청은 항상 서버 A로 보내라" 등의 교통 규칙을 실시간으로 배포합니다.
2. Citadel: 보안 관리 및 신분증 발급
- 역할: 서비스 간 통신의 보안을 책임집니다.
- 하는 일:
- mTLS}$ (Mutual TLS): 서비스들이 서로 통신할 때 쌍방으로 신분증(인증서)을 확인하게 하여 안전한 통신(암호화)을 보장합니다.
- 이 신분증(TLS 인증서)을 발급하고 관리합니다.
3. Gallery: 규칙 관리 및 유효성 검사
- 역할: 서비스 메시의 모든 설정 파일(교통 규칙 문서)을 관리하고 검토합니다.
- 하는 일:
- 관리자가 작성한 규칙(YAML 파일)이 문법적으로 맞는지, 클러스터에 배포해도 문제가 없는지 꼼꼼하게 확인(유효성 검증)하여 안정성을 지킵니다.
- 모든 Envoy 프록시가 일관된 설정을 가지도록 배포를 관리합니다.
🚨 istiod : 교통 관제 센터의 통합
이전에 Istio의 제어 영역(Control Plane)은 여러 개의 독립적인 직원들이 각자 다른 일을 하는 복잡한 구조였습니다. 마치 교통 경찰서, 보안 관리소, 규칙 관리팀이 따로 운영되는 것과 같았죠.
| 이전의 직원 (컴포넌트) | 담당 업무 |
| Pilot | 길 안내 규칙 설정 |
| Citadel | 보안/신분증 발급 |
| Galley | 규칙 문서 검토 및 배포 |
| Mixer | 정책 및 모니터링 |
istiod의 변화 (Istio 1.5/1.6부터)
istiod는 이 모든 복잡한 직원을 하나의 유능한 통합 관리자 (단일 프로세스)로 만든 것입니다.
- 변화: Pilot, Citadel, Galley, Mixer 등의 역할을 istiod 하나가 모두 처리합니다.
istiod 도입의 장점
- 단일화된 컨트롤 플레인: 복잡하게 여러 직원을 관리할 필요 없이, 하나의 관제 센터만 관리하면 됩니다.
- 리소스 절감: 여러 프로그램이 따로 돌아갈 때보다 컴퓨터 자원(CPU, 메모리)을 덜 사용합니다.
- 배포 및 운영의 간소화: 설치하고 관리하기가 훨씬 단순하고 쉬워집니다.
- 성능 향상: 통합되면서 통신 오버헤드가 줄어들어 더 빠르고 효율적으로 작동합니다.
[환경세팅]
k8s 환경 준비
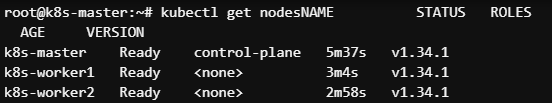
Q) kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=172.16.0.0/16 에서 master/worker 의 ip 대역들이 172.31.0.0/16 대역인데 pod network 대역과 노드들의 ip 대역이 달라도 조이이 되는건가요?
네, ${kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr}$로 지정하는 Pod Network 대역(${172.16.0.0/16}$)과 Master/Worker 노드들의 IP 대역(${172.31.0.0/16}$)이 달라도 클러스터 구성 및 노드 조인에는 전혀 문제없습니다.
Pod Network CIDR의 역할
${--pod-network-cidr}$로 지정하는 대역은 Kubernetes 클러스터 내부에서 Pod들에게 할당될 IP 주소의 범위(CIDR)를 정의합니다.
- Pod IP: 이 대역 내의 IP는 오직 Pod 간의 통신에만 사용됩니다.
- 노드 IP와의 분리: 이 대역은 Master/Worker 노드들이 사용하는 호스트 네트워크 IP(${172.31.0.0/16}$)와는 별개로 작동하며, 충돌을 피하기 위해 달라야 합니다.
노드 IP의 역할
Master/Worker 노드들의 IP 대역(${172.31.0.0/16}$)은 호스트 네트워크에서 노드를 식별하고, 다음과 같은 용도로 사용됩니다.
- 노드 간 통신: ${kubelet}$, ${API Server}$, ${etcd}$ 등의 Kubernetes 컴포넌트 간 통신에 사용됩니다.
- Pod IP 라우팅: CNI (Container Network Interface) 플러그인이 이 노드 IP를 사용하여 Pod Network 대역($\text{172.16.0.0/16}$)으로 향하는 트래픽을 올바른 노드로 라우팅하도록 설정합니다.
결론
Master/Worker 노드는 ${172.31.0.0/16}$ 대역에서 서로 통신하며 클러스터를 형성하고, 일단 클러스터가 형성된 후에는 CNI 플러그인이 ${172.16.0.0/16}$ 대역을 Pod에게 할당하고 노드 간의 통신 경로를 설정합니다. 이 두 대역은 역할이 완전히 분리되어 있으므로 다르게 설정되어야 정상적인 클러스터 구성입니다.
Istio 설치

[실습]
- nginx 파드에 Envoy Proxy 컨테이너를 Sidecar 패턴으로 주입하여, nginx 서비스로 들어오고 나가는 모든 네트워크 트래픽을 Istio의 Control Plane 즉,istiod이 설정한 규칙에 따라 제어하고 모니터링할 수 있게 하는 것
Sidecar Injection
💉 인젝션(Injection)이란 무엇인가요?
인젝션(Injection)은 주입(注入)이라는 뜻으로, Istio에서는 Kubernetes의 Pod 정의에 Envoy Proxy 컨테이너 및 관련 초기화 설정을 자동으로 추가하는 과정을 말합니다.
왜 인젝션을 하나요?
Istio의 모든 기능(트래픽 제어, 보안, 모니터링 등)은 Envoy Proxy를 통해서만 작동합니다. 따라서, Kubernetes 클러스터에서 Istio의 관리를 받으려는 모든 서비스 파드는 반드시 Envoy Proxy를 Sidecar 형태로 가지고 있어야 합니다.
인젝션의 두 가지 방법
| 방법 | 설명 |
| 수동 인젝션 Manual |
istioctl kube-inject 명령을 사용해 yaml 파일을 수동으로 수정한 후 배포합니다. |
| 자동 인젝션 Automatic |
Namespace에 istio-injection=enabled 라벨을 붙이면, Admission Webhook이 Pod 생성 시점에 자동으로 Envoy를 삽입해 줍니다.(일반적으로 운영 환경에서 선호되는 방식) |
1. 수동으로 Sidecar Container 주입
# 샘플 Deploy yaml 생성
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# cat <<EOF > injection-deployment.yaml
> apiVersion: apps/v1
> kind: Deployment
> metadata:
> name: injection-deployment
> spec:
> replicas: 1
> selector:
> matchLabels:
> app: nginx
> template:
> metadata:
> labels:
> app: nginx
> spec:
> containers:
> - name: nginx
> image: nginx:latest
> ports:
> - containerPort: 80
> EOF
# 위 yaml로 배포
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# kubectl apply -f injection-deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/injection-deployment created
# 배포확인
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# kubectl get pod,deploy
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/injection-deployment-6f9664446b-6vw8n 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 4s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/injection-deployment 0/1 1 0 4s
# 수동 인젝션
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# istioctl kube-inject -f injection-deployment.yaml | kubectl apply -f -
deployment.apps/injection-deployment configured
# 인젝션되어 Pod 에 컨테이너가 2개인채로 재배포 되었는지 확인
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
injection-deployment-5d99c86546-tf4mg 1/2 PodInitializing 0 8s
injection-deployment-6f9664446b-6vw8n 1/1 Running 0 16s
2. 자동으로 Sidecar Container 주입 설정
# default 네임스페이스에 자동 인젝션 활성화
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
namespace/default labeled
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
> apiVersion: v1
> kind: Service
> metadata:
> name: nginx
> labels:
> app: nginx
> spec:
> ports:
> - port: 80
> name: http
> selector:
> app: nginx
> ---
> apiVersion: apps/v1
> kind: Deployment
> metadata:
> name: nginx
> spec:
> replicas: 2
> selector:
> matchLabels:
> app: nginx
> template:
> metadata:
> labels:
> app: nginx
> spec:
> containers:
> - name: nginx
> image: nginx
> ports:
> - containerPort: 80
> EOF
service/nginx created
deployment.apps/nginx created
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
injection-deployment-5d99c86546-tf4mg 2/2 Running 0 79s
nginx-7ccccd94f7-5xnhg 1/2 PodInitializing 0 5s
nginx-7ccccd94f7-rzv2l 2/2 Running 0 5s
3. 자동으로 Sidecar Container 주입 설정 후 주입되지 않도록 설정
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
injection-deployment-5d99c86546-tf4mg 2/2 Running 0 2m16s
nginx-7ccccd94f7-5xnhg 2/2 Running 0 62s
nginx-7ccccd94f7-rzv2l 2/2 Running 0 62s
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# kubectl describe pod nginx-7ccccd94f7-5xnhg | grep -A 2 "Init Containers"
Init Containers:
istio-init:
Container ID: containerd://e00b821c29585f7a62812035cc7bd1c2dad5637ab3075a4c2ab272d1e124cb8e
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# kubectl exec nginx-7ccccd94f7-5xnhg -c istio-proxy -- curl http://nginx
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 615 100 615 0 0 77828 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 87857
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
> apiVersion: apps/v1
> kind: Deployment
> metadata:
> name: deny-injection
> spec:
> replicas: 1
> selector:
> matchLabels:
> app: nginx
> template:
> metadata:
> labels:
> app: nginx
> sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false" # 자동 인젝션의 예외 처리
> spec:
> containers:
> - name: nginx
> image: nginx
> ports:
> - containerPort: 80
> EOF
deployment.apps/deny-injection created
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# kubectl get pod,deploy
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/deny-injection-7648569867-hxnpq 1/1 Running 0 5s
pod/injection-deployment-5d99c86546-tf4mg 2/2 Running 0 3m33s
pod/nginx-7ccccd94f7-5xnhg 2/2 Running 0 2m19s
pod/nginx-7ccccd94f7-rzv2l 2/2 Running 0 2m19s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/deny-injection 1/1 1 1 5s
deployment.apps/injection-deployment 1/1 1 1 3m41s
deployment.apps/nginx 2/2 2 2 2m19s
Traffic Management
트래픽 관리는 마이크로서비스 간의 트래픽 흐름을 제어하고 최적화하는 핵심 기능입니다. 이를 위해 다음과 같은 주요 API 리소스를 사용합니다.
- Virtual Service
- Gateway
- Destination Rule
Virtual Service와 Destination Rule의 관계
- Virtual Service는 "트래픽을 어디로 보낼지"에 초점을 맞춥니다.
- Destination Rule은 "도착한 트래픽을 어떻게 처리할지"에 초점을 맞춥니다.(예: "버전 v2 서브셋은 최대 연결 수를 10개로 제한한다")
1. Gateway & VertualService
1. 간단한 hello-world 애플리케이션 배포
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hello-world
labels:
app: hello-world
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5678
selector:
app: hello-world
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Hello, Istio!"
EOF
2. 생성확인
kubectl get pod,svc
3. 외부 트래픽을 받아들일 Ingress Gateway를 설정
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: hello-world-gateway
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- "*"
EOF
4. 생성확인
kubectl get gw
5. Gateway에서 들어온 트래픽을 hello-world 서비스로 라우팅하기 위해 VirtualService를 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- hello-world-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
exact: /hello
route:
- destination:
host: hello-world
port:
number: 80
EOF
6. 생성확인
kubectl get vs
7. 외부 접근하기 위한 노트포트 확인
kubectl get svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway
8. 노드포트로 접근 테스트 (+ 웹브라우저에서도 테스트)
# root@k8s-worker2:~# curl ifconfig.io
# 13.124.241.98
curl http://<ANY-WORKERNODE-EXTERNALIP:NODEPORT>/hello
Hello, Istio!1. hello-world 애플리케이션 배포
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hello-world
labels:
app: hello-world
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5678
selector:
app: hello-world
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Hello, Istio!"
EOF
2. goodbye-world 애플리케이션 배포
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: goodbye-world
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5678
selector:
app: goodbye-world
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: goodbye-world
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: goodbye-world
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: goodbye-world
spec:
containers:
- name: goodbye-world
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Goodbye, Istio!"
EOF
3. 다중 경로 처리 VirtualService 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: hello-world-multi-path
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- hello-world-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
exact: /hello
route:
- destination:
host: hello-world
port:
number: 80
- match:
- uri:
exact: /goodbye
route:
- destination:
host: goodbye-world
port:
number: 80
EOF
4. /hello 경로와 /goodbye 경로 요청 테스트 (NodePort는 Task 1 에서 사용한 포트)
curl http://<ANY-WORKERNODE-EXTERNALIP:NODEPORT>/hello
curl http://<ANY-WORKERNODE-EXTERNALIP:NODEPORT>/goodbye3.트래픽 분할 및 카나리 배포
1. hello-world 애플리케이션 배포
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hello-world
labels:
app: hello-world
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5678
selector:
app: hello-world
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Hello, Istio!"
EOFcat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-world-v2
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world-v2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world-v2
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world-v2
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Hello, Istio! (v2)"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hello-world-v2
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5678
selector:
app: hello-world-v2
EOF
3. 배포 확인
kubectl get pod
4. 트래픽 분할 설정 VirtualService 배포
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: hello-world-canary
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- hello-world-gateway
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: hello-world
port:
number: 80
weight: 80
- destination:
host: hello-world-v2
port:
number: 80
weight: 20
EOF
5. 아래 명령으로 10번정도 요청 시도 (Task1,2 에서 사용한 포트)
curl http://<ANY-WORKERNODE-EXTERNALIP:NODEPORT>
4.Fault Injection
1. hello-world 애플리케이션 배포
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Hello, Istio!"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5678
selector:
app: hello-world
EOF
2. VirtualService 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- hello-world-gateway
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: hello-world
port:
number: 80
EOF
3. 동작 테스트
curl http://<ANY-WORKERNODE-EXTERNALIP:NODEPORT>/hello
4. 지연 주입
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- hello-world-gateway
http:
- fault:
delay:
percentage:
value: 50 # 50%의 요청에 대해 지연 주입
fixedDelay: 5s # 5초 지연
route:
- destination:
host: hello-world
port:
number: 80
EOF
5. 해당 명령을 여러번 사용하여 동작 확인
curl http://<ANY-WORKERNODE-EXTERNALIP:NODEPORT>/hellocat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- hello-world-gateway
http:
- fault:
abort:
percentage:
value: 20 # 20%의 요청에 대해 오류 주입
httpStatus: 500 # HTTP 500 오류 발생
route:
- destination:
host: hello-world
port:
number: 80
EOF
7. 해당 명령을 여러번 사용하여 동작 확인
curl http://<ANY-WORKERNODE-EXTERNALIP:NODEPORT>/helloroot@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
fault filter abortroot@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
fault filter abortroot@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3#
5. Subsets
1.hello-world 애플리케이션 배포
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-world-v1
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world
version: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Hello, Istio v1!"
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-world-v2
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world
version: v2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world
version: v2
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Hello, Istio v2!"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
selector:
app: hello-world
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5678
EOFcat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: hello-world-destination
spec:
host: hello-world
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
EOF
3. VirtualService 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- hello-world-gateway
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: hello-world
subset: v1
weight: 80
- destination:
host: hello-world
subset: v2
weight: 20
EOFcurl http://<ANY-WORKERNODE-EXTERNALIP:NODEPORT>/helloroot@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v1!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v1!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v1!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v2!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v2!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v1!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v2!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v1!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v1!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v2!
6. Loadbalancing
1. Hello world 애플리케이션 배포
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-world-v1
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world
version: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Hello, Istio v1!"
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-world-v2
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world
version: v2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world
version: v2
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Hello, Istio v2!"
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-world-v3
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world
version: v3
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world
version: v3
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Hello, Istio v3!"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
selector:
app: hello-world
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5678
EOF
2.로드밸런싱 기능이 포함된 Destination Rule 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: hello-world-lb
spec:
host: hello-world
trafficPolicy:
loadBalancer:
simple: RANDOM
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
- name: v3
labels:
version: v3
EOF3. VirtualService 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- hello-world-gateway
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: hello-world
EOF
4. 아래 명령으로 10번 정도 테스트 수행
curl http://<ANY-WORKERNODE-EXTERNALIP:NODEPORT>/hello
5. 알고리즘을 최소연결로 변경 또는 ROUND_ROBIN 으로 변경 후 테스트
kubectl edit dr hello-world-lb trafficPolicy:
loadBalancer:
simple: LEAST_CONN #해당 부분root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v1!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v3!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v1!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v2!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v2!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v3!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v3!
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello
Hello, Istio v1!
7. Mirroring
1. 두 개의 APP 배포
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: service-a
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: service-a
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: service-a
spec:
containers:
- name: service-a
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Hello from Service A!"
ports:
- containerPort: 5678
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: service-a
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5678
selector:
app: service-a
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: service-b
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: service-b
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: service-b
spec:
containers:
- name: service-b
image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=Hello from Service B!"
ports:
- containerPort: 5678
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: service-b
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5678
selector:
app: service-b
EOF
2.미러링 Vertual Service 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: mirroring
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- hello-world-gateway
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: service-a
mirror:
host: service-b
mirrorPercentage:
value: 100
EOF
3. 반복문을 사용하여 테스트
while true; do curl http://<ANY-WORKERNODE-EXTERNALIP:NODEPORT>/hello; sleep 0.1; doneroot@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# while true; do curl http://13.124.241.98:32342/hello; sleep 0.1; done
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
Hello from Service A!
4. 확인 후 반복명령 종료
ctrl + C 키 입력
Istio Observability
Istio Observability는 마이크로서비스 환경에서 애플리케이션의 상태와 성능을 모니터링하고 문제를 진단하는 데 필수적인 기능을 제공
1. Kiali Dashboard
-
kiali 설치를 위한 Promtheus & Grafana 설치
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.23/samples/addons/prometheus.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.23/samples/addons/grafana.yaml
2. Kiali 설치
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.23/samples/addons/kiali.yamlkubectl get pods -n istio-system
4. kiali 서비스를 NodePort로 수정
kubectl edit svc -n istio-system kiali
5. kiali 접속 포트 확인
kubectl get svc -n istio-system kiali
2. Bookinfo Application 배포
- 리소스 배포
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
2. 상태 확인
kubectl get pod,svckubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -l app=ratings -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')" -c ratings -- curl -sS productpage:9080/productpage | grep -o "<title>.*</title>"4. GW, VS 배포
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
5. 접속 노트포트 확인
kubectl get svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway80포트에 해당하는 노드포트 확인
curl ifconfig.io
http://<노드의 공인 ip>:<위에서 확인한 노드포트>/productpage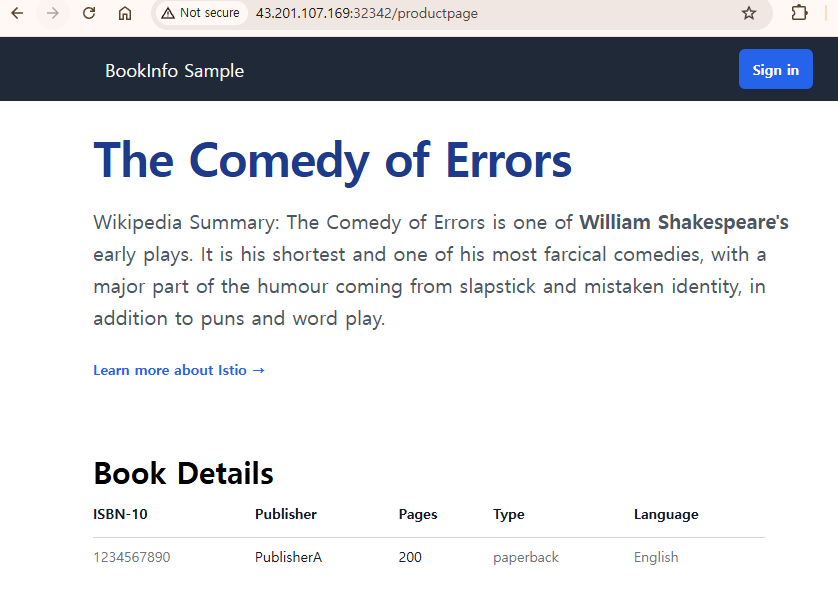
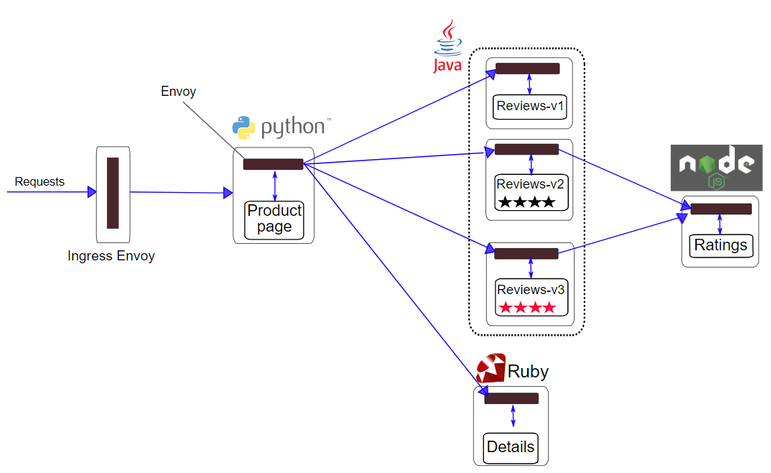
9. kiali 에서 확인
3. Request Routing
-
버전 라우팅 제어를 위해 Destination Rule 생성
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all-mtls.yamlkubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-all-v1.yaml
3.bookinfo 웹 새로고침 시도
4. Kiali에서 트래픽 흐름 확인
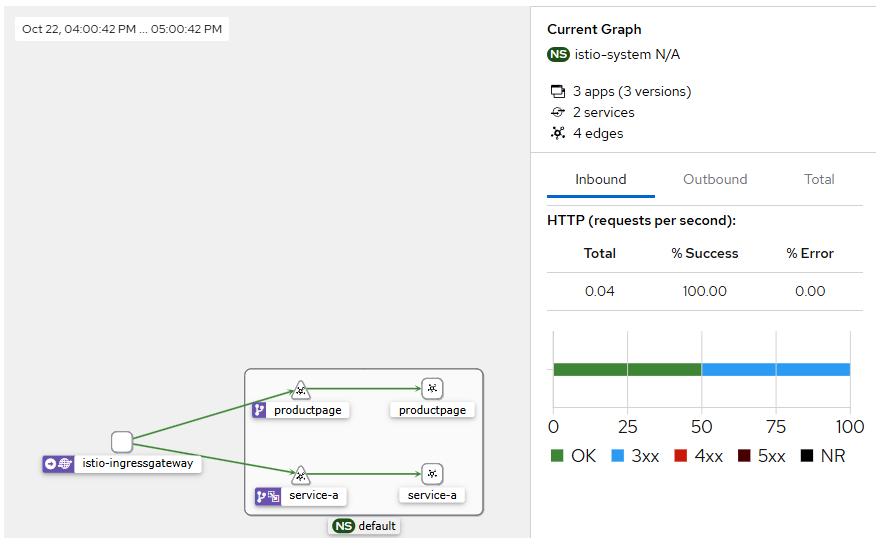
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-test-v2.yaml
6. username : jason 으로 암호는 아무 암호를 입력하여 로그인
1. httpbin 샘플 배포
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.20/samples/httpbin/httpbin.yaml
2. 서킷브레이킹 설정 Destination Rule 생성
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: httpbin
spec:
host: httpbin
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
tcp:
maxConnections: 1
http:
http1MaxPendingRequests: 1
maxRequestsPerConnection: 1
outlierDetection:
consecutive5xxErrors: 1
interval: 1s
baseEjectionTime: 3m
maxEjectionPercent: 100
EOF
3.간단한 부하 테스트 클라이언트 fortio 배포
kubectl apply -f samples/httpbin/sample-client/fortio-deploy.yaml
4.Pod 변수 등록
export FORTIO_POD=$(kubectl get pods -l app=fortio -o 'jsonpath={.items[0].metadata.name}')
5. Pod 에 접속하여 fortio를 사용하여 호출 테스트
kubectl exec "$FORTIO_POD" -c fortio -- /usr/bin/fortio curl -quiet http://httpbin:8000/get
6. 2개의 연결로 20개의 요청 트래픽 테스트
kubectl exec "$FORTIO_POD" -c fortio -- /usr/bin/fortio load -c 2 -qps 0 -n 20 -loglevel Warning http://httpbin:8000/get
7 . 동시연결 3개, 30개 요청 테스트
kubectl exec "$FORTIO_POD" -c fortio -- /usr/bin/fortio load -c 3 -qps 0 -n 30 -loglevel Warning http://httpbin:8000/get
8 . 통계 쿼리 확인
kubectl exec "$FORTIO_POD" -c istio-proxy -- pilot-agent request GET stats | grep httpbin | grep pendingroot@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3# kubectl exec "$FORTIO_POD" -c istio-proxy -- pilot-agent request GET stats | grep httpbin | grep pending
cluster.outbound|8000||httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local;.circuit_breakers.default.remaining_pending: 1
cluster.outbound|8000||httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local;.circuit_breakers.default.rq_pending_open: 0
cluster.outbound|8000||httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local;.circuit_breakers.high.rq_pending_open: 0
cluster.outbound|8000||httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local;.upstream_rq_pending_active: 0
cluster.outbound|8000||httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local;.upstream_rq_pending_failure_eject: 0
cluster.outbound|8000||httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local;.upstream_rq_pending_overflow: 26
cluster.outbound|8000||httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local;.upstream_rq_pending_total: 9
root@k8s-master:~/istio-1.27.3#
현재 상태
- remaining_pending: 1과 rq_pending_overflow: 26 수치를 볼 때, httpbin 서비스의 최대 요청 대기열 설정이 매우 작거나 max pending requests, 또는 이전에 대규모 트래픽 부하 테스트가 진행되어 이미 26개의 요청이 서킷 브레이커 규칙에 의해 overflow되어 차단되었다는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
- 이는 Istio의 Destination Rule을 통해 설정된 서킷 브레이커가 httpbin Service의 과부하를 방지하기 위해 정상적으로 작동하고 있음을 보여줍니다.
'IT > Container&k8s' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [k8s] K8S CICD (0) | 2025.03.30 |
|---|---|
| AWS VPC CNI (1) | 2024.11.03 |
| K8S Cilium CNI (4) | 2024.10.27 |
| K8S Service Mesh Istio (8) | 2024.10.20 |
| K8s Gateway API (0) | 2024.10.13 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- PYTHON
- AI
- VPN
- handson
- ai 엔지니어링
- NFT
- S3
- k8s cni
- operator
- 혼공챌린지
- terraform
- 파이썬
- k8s
- GKE
- cloud
- 도서
- 혼공파
- autoscaling
- GCP
- AWS
- k8s calico
- SDWAN
- AI Engineering
- IaC
- NW
- EKS
- 혼공단
- cni
- CICD
- security
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
